 Overview
Overview
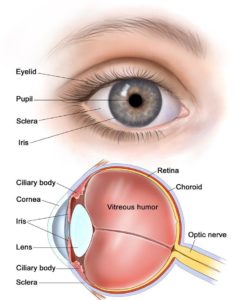
The ratina is a lining of nervous tissues located at the back of the two eyes. It is a photosensitive layer, that is, it is responsible for sensing light and forming images.
Cancer of the ratin is called retinoblastoma. It can occur at any age. It can apprear in any one of the eye, or both the eyes. Usually, the tumor is confined to the eye socket without spreading to the adjascent tissues.
Retinoblastoma has a tendency to be hereditary. This type of cancer often is seen in children.
Symptoms
Usually the tumor id quite evident, with the patient having a white or discolured bulging tumor in one or both eyes, which may have no vision at all.
Risk factors
Age – Eye cancer predominantly found in children and is rarely seen inadults.
Genetic factors – About half the cases of retinoblastoma are hereditary. The other half may occur due to other reasons. Hereditary retinoblastoma tends to affect both the eyes whereas the sporadic ones usually ocuurs only in one eye.
Diagnosis as per modern science
As per modern science diagnosis may involve CT Scan, MRI, Sonography of the abdomen, Bone scan, Biopsy etc.
Staging
Intraoccular retinoblastoma – Cancer is restricted to one or both eyes and has not spred to adjascent or distant tissues.
Extraoccular retinoblastoma – Cancer has spread beyond the eyes, either in adjascent tissues or to distant organs.
Recurrant retinoblastoma – This is a disease which has recurred after the initial therapy is completed. It may have occurred in the eye or in any other part of the body.

 Overview
Overview