 Overview
Overview
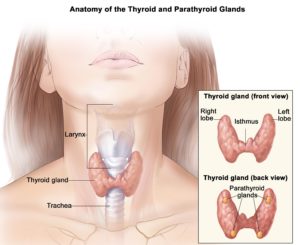
Thyroid cancer is a disease in which cancer cells are found in the tissues of the thyroid gland. the thyroid gland is at the base of the throat. It has two lobes, one on the right side and one on the left. The thyroid gland makes important hormones and helps the body function normally.
There are four main types of thyroid cancer
- papillary
- follicular
- medullary
- anaplastic
Some types of thyroid cancer grow faster than others. The prognosis is better for patients younger than 40 years who have cancer that has not spread beyond the thyroid.
The genes in our cells carry the hereditary information from our parents. An abnormal gene has been found in patients with some forms of thyroid cancer. If medullary thyroid cancer is found, the patient may have been born with a certain abnormal gene which may have led to the cancer. Family members may have also inherited this abnormal gene. Tests have been developed to determine who has the genetic defect long before any cancer appears. It is important that the patient and his or her family members see a doctor about tests that will show if the abnormal gene is present.
Risk factors
Certain factors may increase the risk of developing thyroid cancer.
- Thyroid cancer occurs more often in people between the ages of 25 and 65 years.
- People who have been exposed to radiation or received radiation treatments to the head and neck during infancy or childhood have a greater chance of developing thyroid cancer. The cancer may occur as early as 5 years after exposure or may occur 20 or more years later.
- People who have had goiter (enlarged thyroid) or a family history of thyroid disease have an increased risk of developing thyroid cancer.
- Thyroid cancer is more common in women than in men.Asian people have an increased risk of developing thyroid cancer.
Signs & Symptoms
- A lump in the front of the neck, near the Adam’s apple
- Hoarseness
- Swollen glands in the neck
- Difficulty swallowing
- Difficulty breathing
- Pain in the throat or neck
- A cough that persists and is not caused by a cold
(These symptoms may be caused by thyroid cancer, or they may indicate another less serious condition, such as an infection, benign goiter, or other problem.)
Diagnosis as per modern science
- Fine needle aspiration biopsy
- Thyroid scan
- Ultrasound
- Computed tomography
- MRI
- Blood tests
Staging
Stage I – The cancer is less than 2 cm and has not spread to lymph nodes or distant sites.
Stage II – The cancer is 2 to 4 cm. and has not spread to lymph nodes or distant sites.
Stage III – The cancer is larger than 4 cm or has grown slightly outside the thyroid and has not spread to lymph nodes or distant sites; or it is any size and has spread to local neck nodes but not to distant sites.
Stage IV – Tumor of any size and has grown beyond the thyroid gland to invade nearby tissues of the neck and has spread to lymph nodes in the upper chest, tumor has grown either back to the spine or into nearby large blood vessels, it has spread to distant sites.

 Overview
Overview